What is CFD
CFD (contract for difference) is an abbreviation from English, which stands for "Contract for Difference". CFD is a derivative financial instrument that allows traders to speculate on the price movements of various financial instruments, such as stocks, indices, commodities or currencies, without owning the underlying asset.
When trading CFDs, an investor essentially enters into a contract with a broker to return the difference in the value of an asset from the moment the contract is opened until the moment it is closed. If the asset price moves in a favorable direction, traders make a profit, but if it moves in the opposite direction from the forecast, they incur losses.
One of the key aspects of CFD trading is the ability to use leverage, that is, to open larger positions with a smaller balance on the trading account. This can increase both potential profits, but also increases the risk of losses. The key point here is the ability to manage your capital, compliance with the rules of Money management.
Using this type of financial instrument provides flexibility in trading, since with their help you can open both long positions (make a purchase, assuming that the price will rise) and short positions (make a sale, assuming that the price will fall) on the asset. To better understand the principle of operation, let's look at an example:
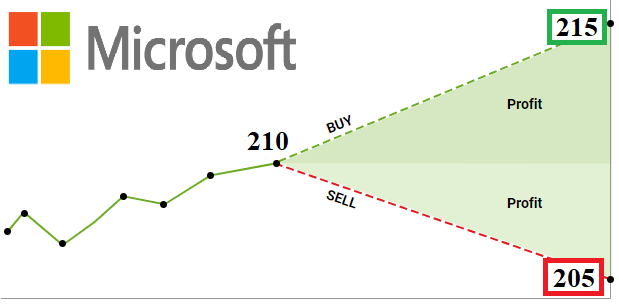
Let's say you believe that Microsoft shares, currently trading at $210 per share, will rise in price over the next few days. Instead of buying the shares outright, you decide to enter into a CFD contract for 100 shares of the company.
If the price rises to $215 per share and you close the CFD position, the difference of $5 per share (from $50 to $55) for 100 shares or $500 will be your profit. Conversely, if the price falls to $205 per share, you will incur a loss of $500 when you close the position.
To learn how to predict the future change in the price of a financial instrument and correctly determine the type of contract (buy or sell), we recommend that you read our article “5 steps for a novice trader”.
Good luck!
